Predicting U.S. Core Inflation Using Machine Learning
Machine_Learning Economics Time_Series Python
Overview
Inflation plays a critical role in financial planning, policymaking, and investment decisions.
Following COVID-19, inflation dynamics became more volatile, reducing the effectiveness of traditional forecasting methods.
This project uses machine learning to predict U.S. core inflation and analyze the macroeconomic factors driving inflation trends.
Project Framework
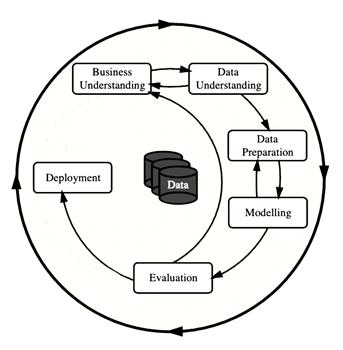
The project follows the CRISP-DM framework, ensuring a structured and business-aligned analytics workflow.
Data Overview
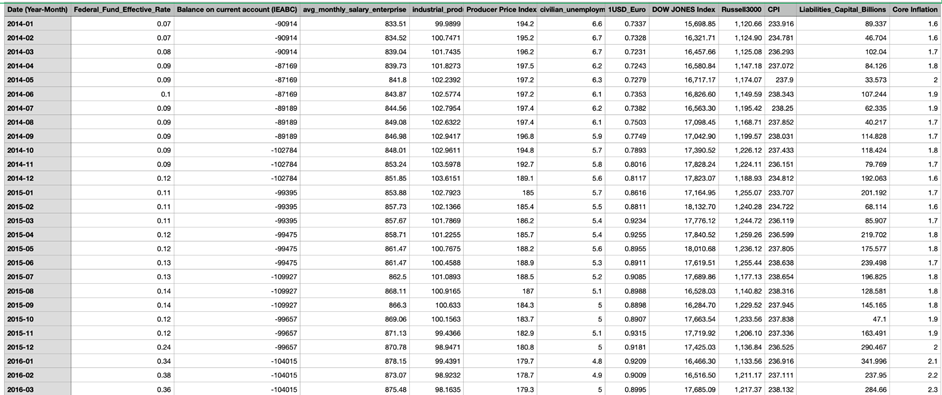
- Time period: Jan 2014 – Jun 2024 (monthly)
- Sources: FRED, BLS, Yahoo Finance, Investing.com
- Target Variable: Core Inflation (excludes food & energy)
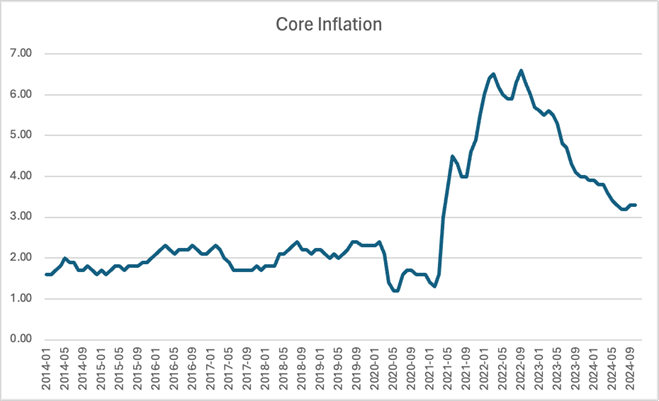
Inflation Trend

The chart shows a sharp rise in inflation beginning in early 2021, largely driven by post-COVID supply shocks and monetary policy changes.
Feature Relationships
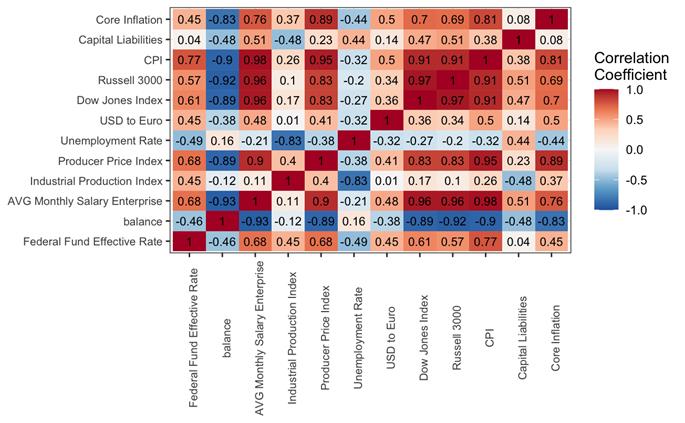
The correlation matrix highlights strong relationships between inflation, interest rates, labor indicators, and equity markets.
Model Architecture
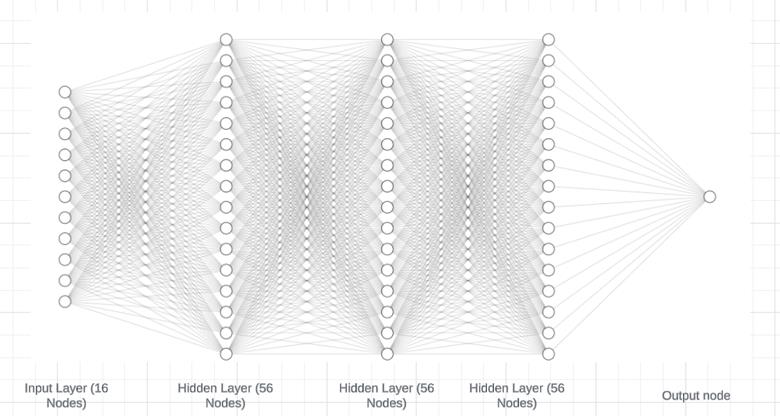

- Neural Network regression model
- 3 hidden layers × 56 neurons (ReLU)
- Adam optimizer, MSE loss
Model Performance
Actual vs Predicted Inflation
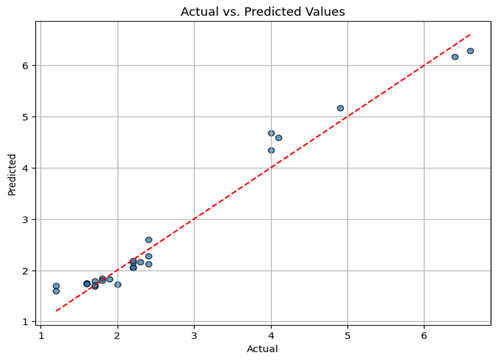
The model performs strongly in low-to-moderate inflation regimes, with tighter clustering around the ideal prediction line.
Residual Analysis
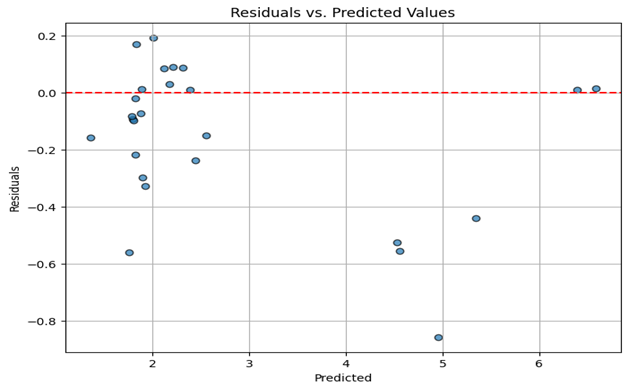
Residuals increase during high-inflation periods, indicating structural regime shifts that are harder to model.
Learning Curves
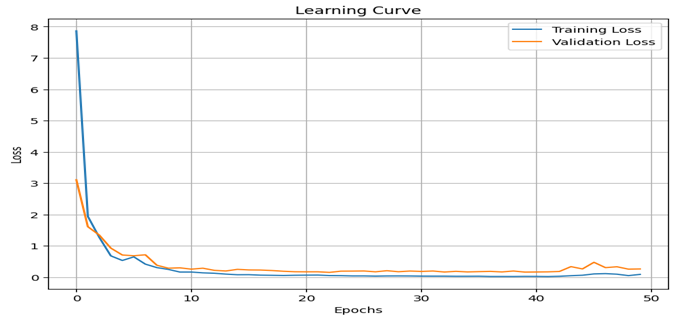
Training and validation losses converge smoothly, suggesting good generalization without overfitting.
Error Distribution
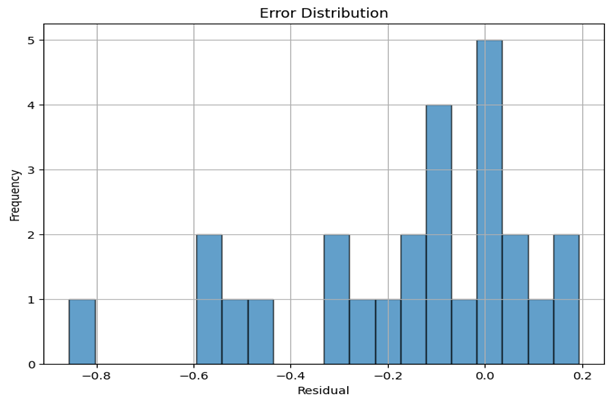
Most prediction errors are centered near zero, with longer tails during extreme inflation periods.
Key Takeaways
- ~93% prediction accuracy
- Strong performance during stable inflation periods
- Useful for policy and scenario analysis, not point forecasting
- Demonstrates practical ML applied to macroeconomic data
Tech Stack
Python · TensorFlow · Keras · scikit-learn · Pandas · NumPy · Matplotlib